Cloning Human Antibodies
Immune responses are among the most effective protection mechanisms against diseases, and antibodies can be effective against neurodegeneration. ISAB integrates a acoustic-dispensing platform (40,000 ELISAs/day) with clinical biobank samples. The goal is to identify disease-relevant signatures, stratify patients using machine learning, and clone protective human antibodies from high-affinity responders.
Large-scale seroepidemiology connects tau autoimmunity and to kidney disease
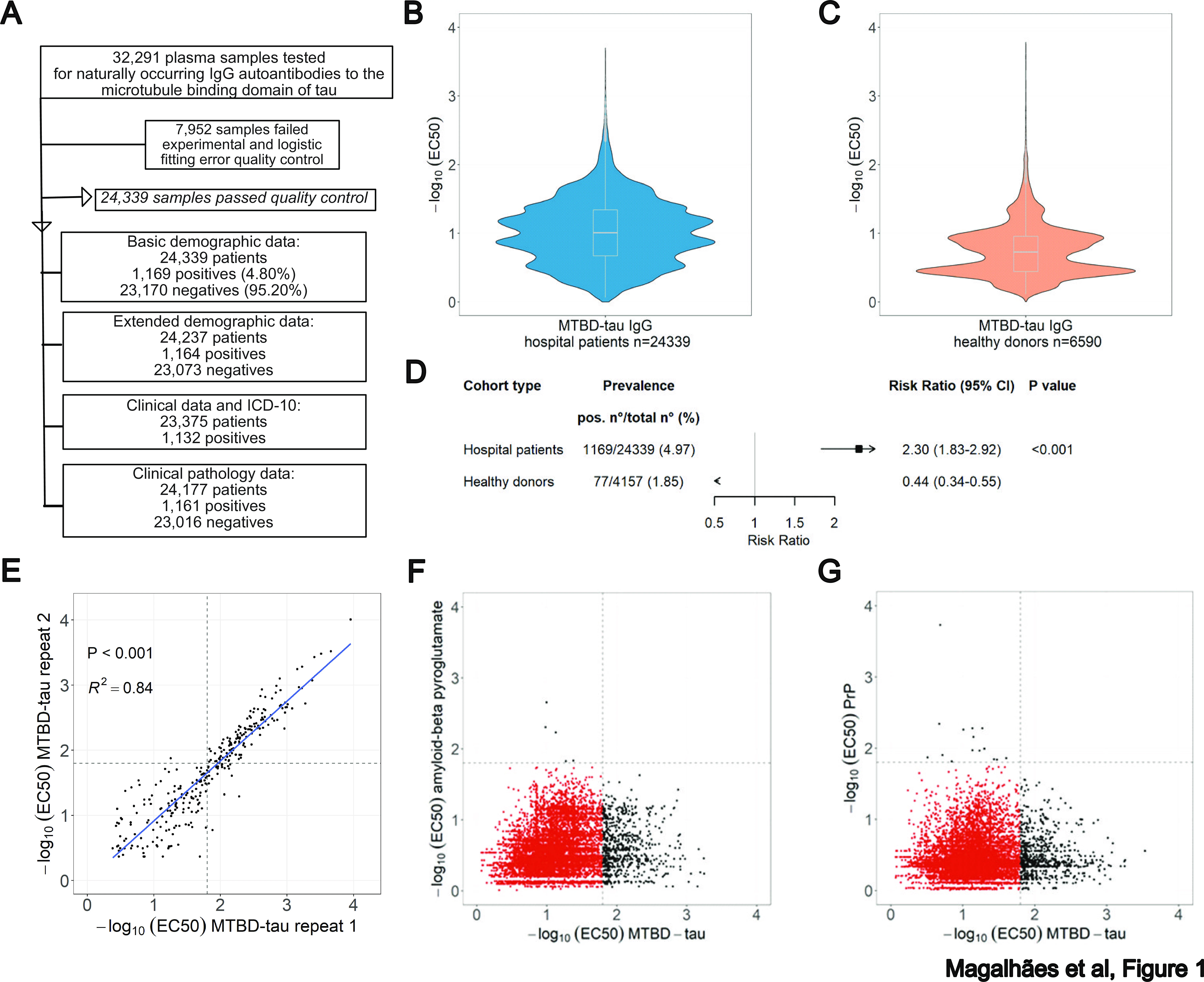
Using our high-throughput acoustic-dispensing microELISA pipeline, we screened large cohorts of human plasma for naturally occurring IgG autoantibodies against the microtubule-binding domain of tau (MTBD-tau). We then linked seroreactivity to clinical diagnoses and laboratory parameters in a hypothesis-free manner.
What we did
- Quantified anti–MTBD-tau IgG using miniaturized, automated microELISAs with dilution-curve quality control.
- Validated antibody specificity using competition assays and controls for nonspecific binding.
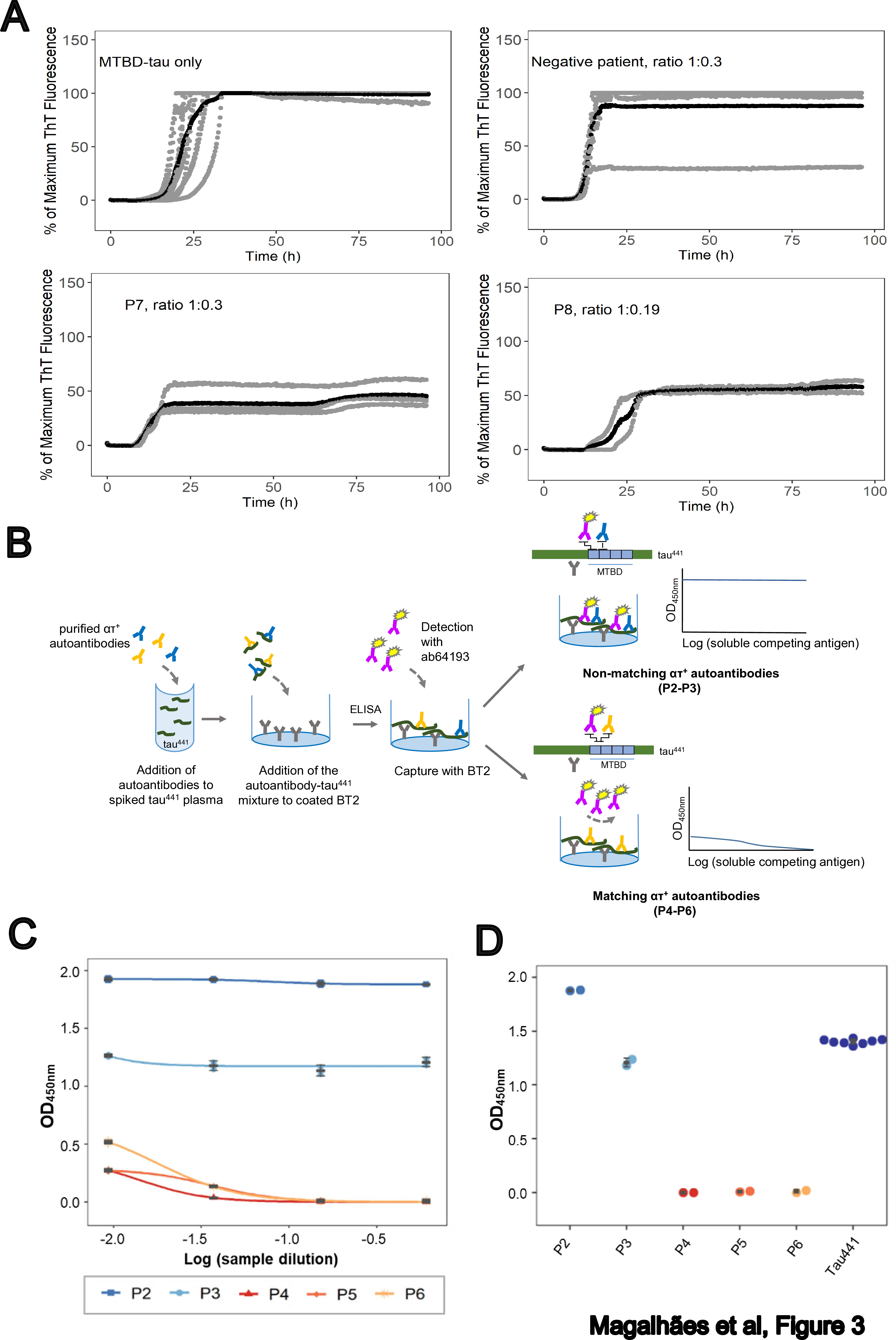
- Purified tau-reactive antibodies from selected donors and tested functional effects on tau aggregation and assay performance.
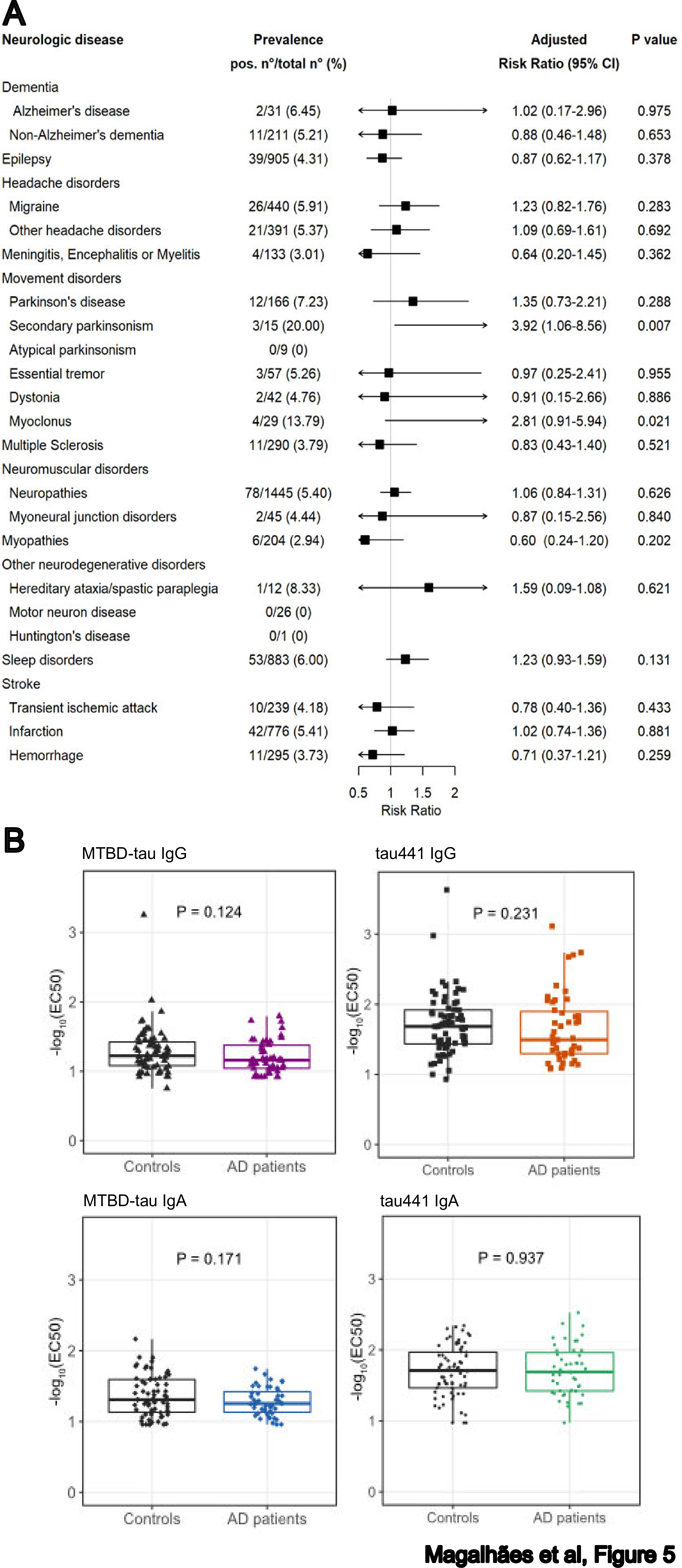
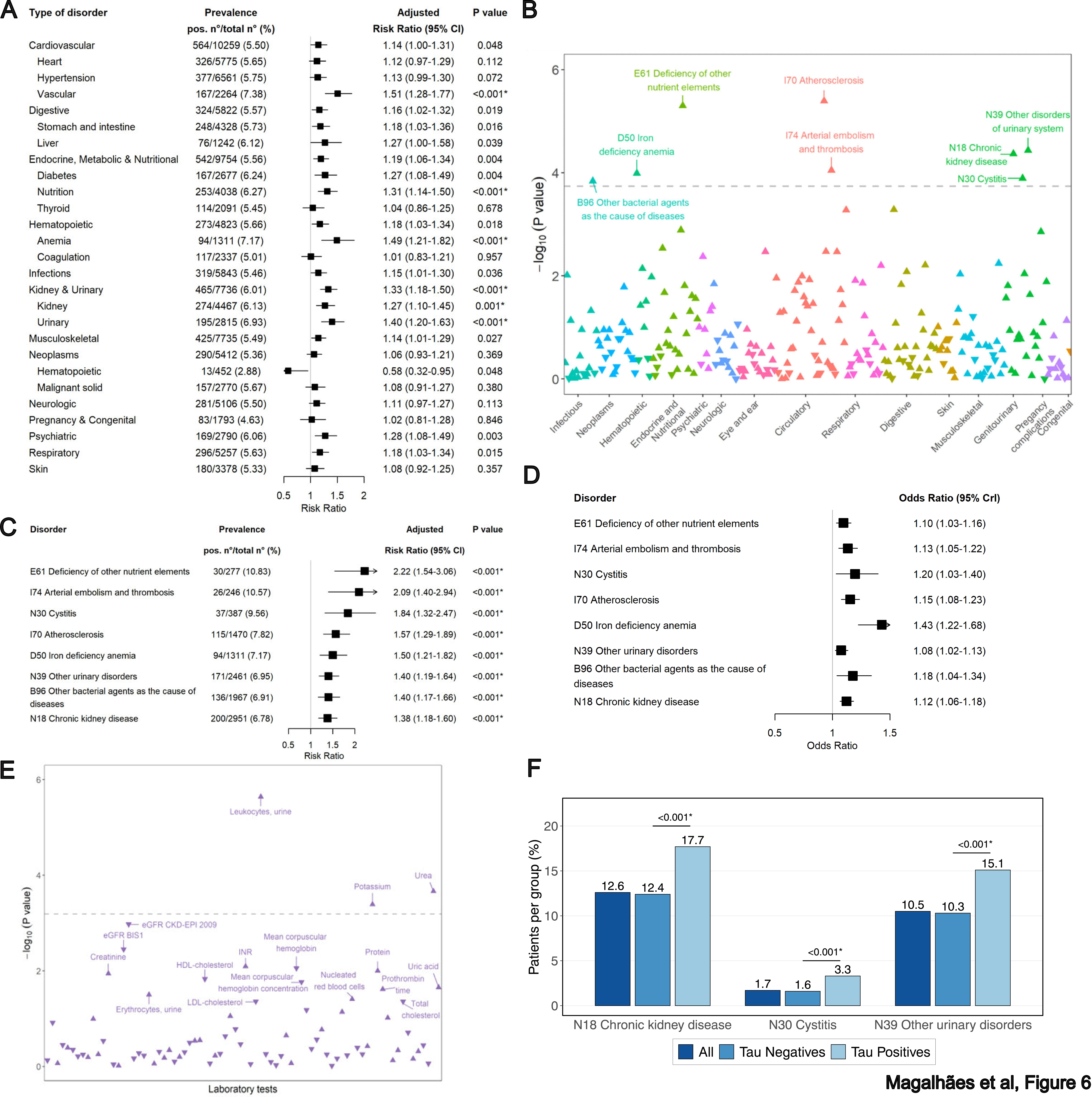
- Performed large-scale association analyses with ICD-10 codes and routine clinical laboratory parameters.
Key findings
- Natural anti-tau antibodies are common and enriched in hospital cohorts compared with healthy donors.
- High specificity: the autoreactive response is directed against tau with limited polyreactivity.
- Functional impact: endogenous antibodies can inhibit tau aggregation and interfere with tau immunoassays.
- No robust association with neurological disease, including Alzheimer's disease.
- Strong association with nephro-urological pathology, supported by clinical diagnoses and laboratory markers.
Why this matters: These results extend tau biology beyond the nervous system and have implications for plasma tau biomarker interpretation and for tau-directed immunomodulatory strategies. As a cross-sectional study, the data do not establish causality.
Reference: Magalhães AD et al. Large-scale seroepidemiology uncovers nephro-urological pathologies in persons with tau autoimmunity. PLOS Biology.